طراحی آنتن تک قطبی مسطح بهینه شده با استفاده از الگوریتم بهینهسازی چند منظوره ترکیبی و توابع آشوبناک
محورهای موضوعی : طراحی و کاربرد آنتن
وحید حسینی
1
![]() ,
یوسف فرهنگ
2
,
یوسف فرهنگ
2
![]() ,
کامبیز مجید زاده
3
,
کامبیز مجید زاده
3
![]() ,
چنگیز قبادی
4
,
چنگیز قبادی
4
![]()
1 - گروه مهندسی کامپیوتر و فناوری اطلاعات، دانشگاه پیام نور، تهران، ایران.
2 - دانشکده مهندسی و معماری، گروه مهندسی کامپیوتر، دانشگاه اسنیورت استانبول، ترکیه.
3 - گروه مهندسی کامپیوتر، واحد ارومیه، دانشگاه آزاد اسلامی، ارومیه، ایران
4 - گروه مهندسی الکترونیک، دانشگاه ارومیه، ارومیه، ایران
کلید واژه: آنتن تک قطبی, الگوریتم بهینهسازی, الگوریتم ازدحام ذرات و الگوریتم ژنتیک, تابع آشوبناک,
چکیده مقاله :
این تحقیق از یک الگوریتم بهینهسازی چند هدفه جدید برای طراحی یک آنتن يك قطبی با ویژگیهای الکترومغناطیسی خاص استفاده میکند. این الگوریتم از یک تابع آشوبناک ترکیبی برای ادغام الگوریتم ازدحام ذرات جهشیافته سفارشی شده با الگوریتم ژنتیک اصلاحشده استفاده مینماید. رویکرد ترکیبی جدید با اجتناب از به دام افتادن در حداقلهای محلی، سریعتر از الگوریتمهای متداول ازدحام ذرات و الگوریتم ژنتیک به نتایج دلخواه نیل مینماید. عملکرد الگوریتم فرا ابتکاری پیشنهادی با استفاده از توابع معیار مانند تابع راستریگن، تابع آکلی، تابع روزنبروک و تابع بووث با موفقیت شبیهسازی و تثبیت شدهاند. در نهایت، اعتبار رویکرد ارائه شده برای کاربردهای الکترومغناطیسی با بهینهسازی یک آنتن تک قطبی مایکرواستریپ مسطح با ساختاری ساده نشان داده میشود، الگوریتم پیشنهادی اجازه میدهد تا معیارهای بهینهسازی طوری سفارشی شوند که به نتایج از پیش در نظر گرفته شده برای افت بازگشتی و فرکانس رزونانس نیل نمایند. الگوریتم بهینهسازی توسعه یافته در متلب، برای تعیین تنظیمات پارامترهای لازم به منظور دستیابی به باندهای فرکانسی مورد انتظار با استفاده از الگوریتم ازدحام ذرات جهشیافته سفارشی یا ژنتیک اصلاح شده ابتکاری استفاده میشود. ابعاد عناصر آنتن پیشنهادی، به طور قابل توجهی بر عملکرد آنتن تأثیر میگذارند.
This research uses a new multi-objective optimization algorithm to design a single pole antenna with specific electromagnetic characteristics. This algorithm uses a hybrid chaotic function to integrate the customized mutated particle swarm algorithm with the modified genetic algorithm. By avoiding getting trapped in local minima, the new hybrid approach achieves desired results faster than conventional particle swarm algorithms and genetic algorithms. The performance of the proposed meta-heuristic algorithm has been successfully simulated and stabilized using benchmark functions such as Rastrigen's function, Ackley's function, Rosenbrook's function, and Booth's function. Finally, the validity of the presented approach for electromagnetic applications is demonstrated by optimizing a planar microstrip monopole antenna with a simple structure. The proposed algorithm allows the optimization criteria to be customized to achieve the predetermined results for return loss and resonance frequency. The optimization algorithm developed in MATLAB is used to determine the necessary parameter settings in order to achieve the expected frequency bands using custom mutated particle swarm algorithm or heuristic modified genetics. The dimensions of the proposed antenna elements significantly affect the antenna performance.
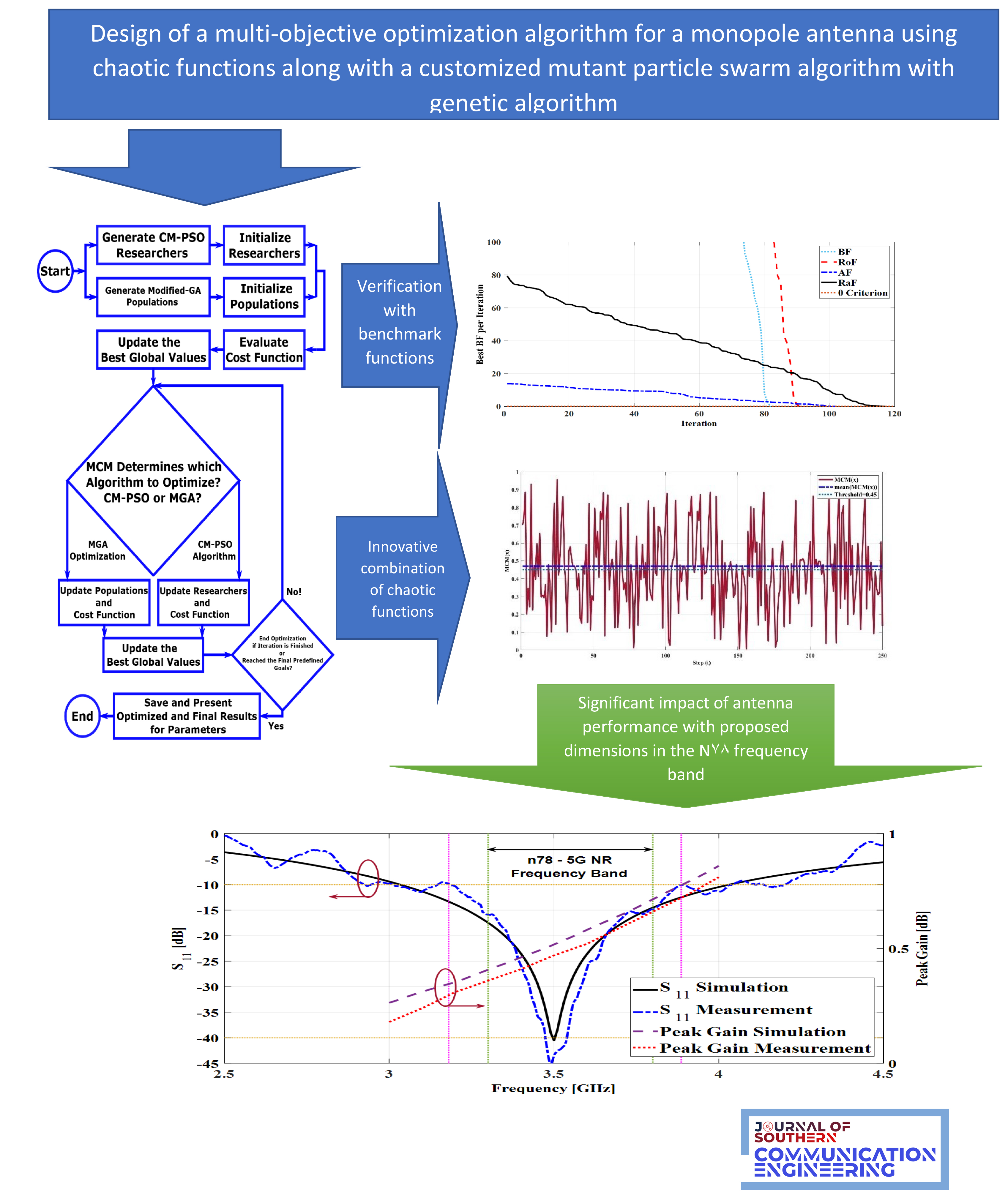
ادغام الگوریتم های فراابتکاری با استفاده از توابع آشوب ناک برای غلبه بر چالش ها در ترکیب الگوریتم ها.
بهبود الگوریتم ژنتیک کلاسیک برای بهبود عملکرد.
توسعه یک الگوریتم بهینه سازی ترکیبی چند هدفه با عملکرد بهتر.
Citation: V. Hosseini, Y. Farhang, K. Majidzadeh, and Ch. Ghobadi, “Multi-Objective Optimization Algorithm Development using Chaotic Maps to Design of a Planar Microstrip Monopole Antenna,” Journal of Southern Communication Engineering, vol. 14, no. 55, pp. 121–142, 2025, doi:10.30495/jce.2023.1985366.1202 [in Persian].
[1] M. Wetter and J. Wright, “A comparison of deterministic and probabilistic optimization algorithms for no smooth simulation-based optimization,” Building and Environment, vol. 39, no. 8, pp. 989–999, 2004, doi: 10.1016/j.buildenv.2004.01.022.
[2] S. Jin, H. Lee and J. Jeong, "Fast partial distortion elimination algorithm based on hadamard probability model," Electronics Letters, vol. 44, no. 1, 2008, doi: 10.1049/el:20082872.
[3] Y. -C. Lin, M. Clauß and M. Middendorf, "Simple Probabilistic Population-Based Optimization," in IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, vol. 20, no. 2, pp. 245-262, April 2016, doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2015.2451701.
[4] R. L. Haupt, "An introduction to genetic algorithms for electromagnetics," in IEEE Antennas and Propagation Magazine, vol. 37, no. 2, pp. 7-15, April 1995, doi: 10.1109/74.382334.
[5] S. M. Mikki and A. A. Kishk, "Quantum Particle Swarm Optimization for Electromagnetics," in IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, vol. 54, no. 10, pp. 2764-2775, Oct. 2006, doi: 10.1109/TAP.2006.882165.
[6] E. BouDaher and A. Hoorfar, "Electromagnetic Optimization Using Mixed-Parameter and Multiobjective Covariance Matrix Adaptation Evolution Strategy," in IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, vol. 63, no. 4, pp. 1712-1724, April 2015, doi: 10.1109/TAP.2015.2398116.
[7] S. M. Mikki and A. A. Kishk, “Particle swarm optimization: A physics-based approach,” Synthesis Lectures on Computational Electromagnetics, vol. 3, pp. 1–103, 2008, doi: 10.2200/s00110ed1v01y200804cem020.
[8] K. Kaboutari, A. Zabihi, B. Virdee and M. Salmasi “Microstrip patch antenna array with cosecant-squared radiation pattern profile,” AEU - International Journal of Electronics and Communications, vol. 106, pp. 82–88, 2019, doi: 10.1016/j.aeue.2019.05.003.
[9] M.H. Teimouri, Ch. Ghobadi, J. Nourinia, K. Kaboutari, M. Shokri and B.S. Virdee “Broadband printed dipole antenna with integrated balun and tuning element for DTV application,” AEU - International Journal of Electronics and Communications, vol. 148, p. 154161, 2022, doi: 10.1016/j.aeue.2022.154161.
[10] M. Shokri et al., "A Printed Dipole Antenna for WLAN Applications with Anti-interference Functionality," Photonics & Electromagnetics Research Symposium (PIERS), Hangzhou, China, 2021, pp. 1486-1494, doi: 10.1109/PIERS53385.2021.9694670.
[11] M. M. Hasan and H. T. Mouftah, "Optimization of Watchdog Selection in Wireless Sensor Networks," in IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, vol. 6, no. 1, pp. 94-97, Feb. 2017, doi: 10.1109/LWC.2016.2633990.
[12] L. Cao, Y. Cai and Y. Yue, "Swarm Intelligence-Based Performance Optimization for Mobile Wireless Sensor Networks: Survey, Challenges, and Future Directions," in IEEE Access, vol. 7, pp. 161524-161553, 2019, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2951370.
[13] D. Cao, A. Modiri, G. Sureka and K. Kiasaleh, "DSP Implementation of the Particle Swarm and Genetic Algorithms for Real-Time Design of Thinned Array Antennas," in IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, vol. 11, pp. 1170-1173, 2012, doi: 10.1109/LAWP.2012.2220514.
[14] A. Modiri and K. Kiasaleh, "Modification of Real-Number and Binary PSO Algorithms for Accelerated Convergence," in IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, vol. 59, no. 1, pp. 214-224, Jan. 2011, doi: 10.1109/TAP.2010.2090460.
[15] F. Grimaccia, M. Mussetta and R. E. Zich, "Genetical Swarm Optimization: Self-Adaptive Hybrid Evolutionary Algorithm for Electromagnetics," in IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, vol. 55, no. 3, pp. 781-785, March 2007, doi: 10.1109/TAP.2007.891561.
[16] A. A. Minasian and T. S. Bird, "Particle Swarm Optimization of Microstrip Antennas for Wireless Communication Systems," in IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, vol. 61, no. 12, pp. 6214-6217, Dec. 2013, doi: 10.1109/TAP.2013.2281517.
[17] B. Tütüncü, “Compact low radar cross-section microstrip patch antenna using particle swarm optimization,” Microwave and Optical Technology Letters, vol. 61, pp. 2288–2294, 2019, doi: 10.1002/mop.31893.
[18] Z. Bayraktar, P. L. Werner and D. H. Werner, "The design of miniature three-element stochastic Yagi-Uda arrays using particle swarm optimization," in IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, vol. 5, pp. 22-26, 2006, doi: 10.1109/LAWP.2005.863618.
[19] D. Ustun, A. Toktas and A. Akdagli, “Deep neural network–based soft computing the resonant frequency of E–shaped patch antennas,” AEU - International Journal of Electronics and Communications, vol. 102, pp. 54–61, 2019, doi: 10.1016/j.aeue.2019.02.011.
[20] G. Singh and U. Singh, “Triple band-notched UWB antenna design using a novel hybrid optimization technique based on DE and NMR algorithms,” Expert Systems with Applications, vol. 184, p. 115299, 2021, doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2021.115299.
[21] W. T. Li, X. W. Shi, Y. Q. Hei, S. F. Liu and J. Zhu, "A Hybrid Optimization Algorithm and Its Application for Conformal Array Pattern Synthesis," in IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, vol. 58, no. 10, pp. 3401-3406, Oct. 2010, doi: 10.1109/TAP.2010.2050425.
[22] V. Hosseini, Y. Farhang, K. Majidzadeh and Ch. Ghobadi, “Customized mutated PSO algorithm of isolation enhancement for printed MIMO antenna with ISM band applications,” AEU - International Journal of Electronics and Communications, vol. 145, no. 2, p. 154067, 2022, doi: 10.1016/j.aeue.2021.154067.
[23] V. H. Hasbestan, Y. Farhang, K. Majidzadeh and C. Ghobadi, "Multi-Objective Hybrid Optimization Algorithm for Design a Printed MIMO Antenna With n78–5G NR Frequency Band Applications," in IEEE Access, vol. 11, pp. 68231-68242, 2023, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3292307.
[24] V. Hosseini et al., "Dual-Band Planar Microstrip Monopole Antenna Design Using Multi-Objective Hybrid Optimization Algorithm," Photonics & Electromagnetics Research Symposium (PIERS), Prague, Czech Republic, 2023, pp. 467-475, doi: 10.1109/PIERS59004.2023.10221360.
[25] M. Masdari, S. Barshande and S. Ozdemir, "CDABC: chaotic discrete artifcial bee colony algorithm for multi level clustering in large scale WSNs," The Journal of Supercomputing, vol. 75, no. 1, pp. 7174–7208 , 2019, doi: 10.1007/s11227-019-02933-3.
[26] S. Barshandeh and M. Haghzadeh, “A new hybrid chaotic atom search optimization based on tree‑seed algorithm and Levy flight for solving optimization problems,” Engineering with Computers, vol. 37, pp. 3079–3122, 2020, doi: 10.1007/s00366-020-00994-0.


